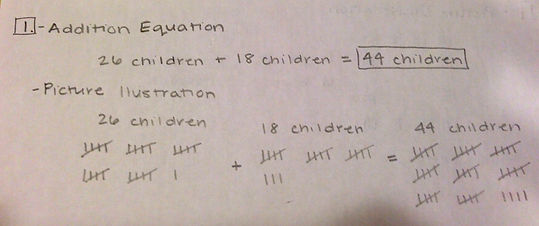Ms. Stults'
Technology Portfolio
Math Problem Portfolio
Springboard Problem for 2nd Grade Math Lessons
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
1. Problem: There are 26 children on the playground. Then 18 more children showed up. How many children are there now?
Common Core Standard: 2.OA.1
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: set up an addition problem; draw a picture,
Mathematical Understanding: This problem helps students develop understanding of one-step addition problems where two groups of items are being combined.
Solution: To solve this problem I first created an addition equation where I added the two groups of children to find the total. My second method was drawing a picture to represent the two groups of children. I then added the two groups together and drew the total number of children.
Web 2.0 Tools: Educreations white board app, Google Draw, Color Chips (nlvm.usu.edu)
2. Problem: There are 29 peas on the plate. Carlos ate 15 peas. His mother put 7 more person the plate. How many peas are on the plate now?
Common Core Standard: 2.OA.1
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: set up a multi-step equation, draw a picture, work with manipulatives
Mathematical Understanding: Students will be working with multi-step equations involving both addition and subtractions. This will utilize both addition and subtraction skills.
Solution: I first wrote out a multi-step addition/subtraction problem that followed the progression of the question (started with 29, then lost 15, then got 7 more) in order to figure out the number of peas left. I then drew a picture to represent the 29 original peas, then I showed 15 peas being taken away, then added 7 peas back to to the plate to represent the ending total of 21 peas.
Web 2.0 Tools: Educreations whiteboard app, Google Draw, “Color Chips” virtual manipulatives (nlvm.usu.edu)
3. Problem: There are some students in the Library. Then 17 more students came. There are now 47 students. How many students were in the Library at the beginning?
Common Core Standard: 2. OA.1
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: draw a picture, set up an equation, use manipulatives
Mathematical Understanding: This problem gives students practice with an addition problem where there is a missing factor. It requires students to look at a total, a given factor, and figure out the original number.
Solution: I first wrote an equation using an unknown factor to represent the problem. “x” represented the unknown starting number of students. I then added 17 to “x” and had the equation equal 47. I then solved the equation to find the value of x, which is 30.
Web 2.0 Tools: Educreations whiteboard app, “Color Chips/Base Blocks” virtual manipulatives (nlvm.usu.edu)
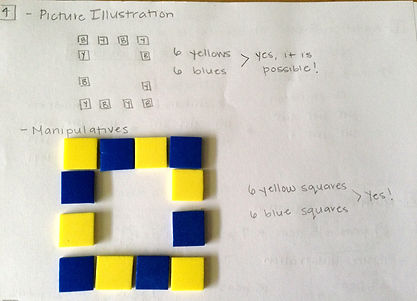
4. Problem: Anna wants to put some blue and yellow tiles on a wall for decoration. She is thinking about several different patterns of tiles she could create. She wants to choose a pattern that would let her use exactly as many blue tiles as yellow tiles. Is it possible to create the pattern below using the same number of blue tiles as yellow tiles?
Common Core Standard: 2.OA.3
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: draw a picture, work with manipulatives
Mathematical Understanding: This problem challenges students to think about even and odd number of objects and how to create patterns using different colored objects. It will help them visualize how the number of objects and variations of objects impacts a pattern.
Solution: I first drew an illustration of this problem and alternated writing “B” or “Y” in the squares to represent their colors. I alternated until each square had a color. I then used manipulatives to answer the question. I mimicked the given pattern using an alternative color pattern. Both of these methods resulted in me finding that Anna could use the same number of blue and yellow tiles in the pattern.
Web 2.0 Tools: Google Draw, Educreations whiteboard app, virtual manipulatives (http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/mathematics/ebook_assets/vmf/VMF-Interface.html)
Number and Operations in Base Ten
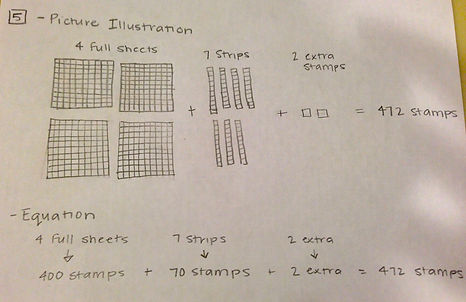
5. Problem: The post office packages stamps like this:
10 stamps in each strip.
10 strips of 10 in each sheet.
Yesterday Mike saw 4 full sheets, 7 strips, and 2 extra stamps in the drawer. He counted all the stamps and found out that there were 472 stamps in all. Why did Mike’s number matchup with the numbers of sheets, strips, and extra stamps?
Common Core Standard: 2.NBT.A.1
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: draw a picture, create an equation
Mathematical Understanding: This problem gives student practice with place values of hundreds, tens, and ones. It also helps students understand that 100 can be thought of as a bundle of ten tens.
Solution: I first drew a picture to represent the addition of four sheets, 7 strips, and 2 extras. Each sheet has 100 stamps and each strip has 10 stamps. My illustration show each stamp and the total number of stamps once the sheets, strips, and extras are added together. My second approach was with an addition equation. I add 400 (represented by 4 full sheets) and 70 stamps (represented by 7 strips) and 2 stamps (the 2 extras) to find that there were a total of 472 stamps.
Web 2.0 Tools: virtual cuisenaire rods (http://nrich.maths.org/4348) , Google Draw, “Place Value” virtual manipulatives (nlvm.usu.edu/), Educreations whiteboard app
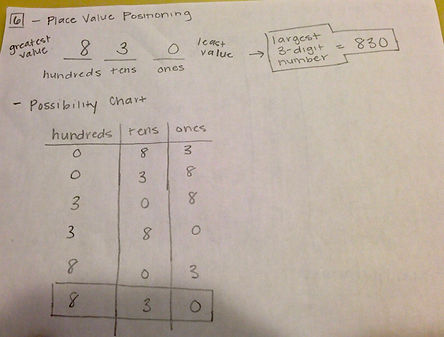
6. Problem: Donna had three cards with the numbers 0, 8, and 3 written on them. Her teacher said: “What is the largest three-digit number you can make?”
Common Core Standard: 2.NBT.1
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: create a chart of possibilities; write numbers in order based on highest value and order
Mathematical Understanding: This problem has students focus on place values and recognizing that the number in the hundreds place holds more value that the numbers in the tens and ones places.
Solution: In my first approached I examined the three numbers I was given and decided to place them from greatest value to least value starting in the hundreds place and moving down to the ones place. My second method was creating a chart of all of the possible number combinations and finding which had the greatest value. In both methods I found 830 to be the answer.
Web 2.0 Tools: excel, Educreations whiteboard app, Google Draw, “Place Value” virtual manipulatives (nlvm.usu.edu)
7. Problem: What number represents the same amount as 2 tens + 7 ones?
Common Core Standard: 2.NBT.1
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: draw a picture, write an addition equation
Mathematical Understanding: This problem utilizes student knowledge of the tens and ones place values. Students must know the 2 tens equals 20 and that 7 ones is equal to 7.
Solution: I first wrote out and solved a simple addition equation to represent the two numbers in the problem. Then a drew a pictures representing the 2 sets of ten and 7 ones and the resulting total of 27 once they were combined.
Web 2.0 Tools: virtual Cuisenaire rods (http://nrich.maths.org/4348), Color Chips/Base Blocks (nlvm.usu.edu), Educreations whiteboard app
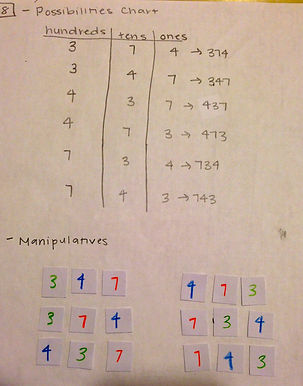
8. Problem: Use all the digits 3, 7, and 4 to create different 3-digit numbers
Common Core Standard: 2.NBT.4
Source: http://www.lakeshore.wnyric.org/cms/lib/NY19001770/Centricity/Domain/432/Corrected.pdf
Methods: create a chart of possibilities, use manipulatives
Mathematical Understanding: This problem has students working with place values. Students must understand the different between the hundreds, tens, and ones spots and the value of the number that is in each position. The student must understand how you an add numbers in each place value together to create three-digit numbers.
Solution: In my first methods I wrote out all of the possible number combinations to make 3-digit numbers. In my second method I used manipulative cards to show different combination of the three given digits.
Web 2.0 Tools: excel, Educreations whiteboard app
Measurement
9. Problem: Juan walked two meters every second. How many meters did Juan walk in five seconds?
Common Core Standard: 2.MD.B.5
Source: http://mrnussbaum.com/grade_2_standardslengthwordproblems/
Methods: draw a representative diagram, set up a proportion
Mathematical Understanding: Students will be working with equations to solve problems involving lengths that are given in the same units (ex. meters). Students will get experience writing equations with a symbol for the unknown number.
Solution: I first drew a picture representing the number of meters Juan walked each second. In the diagram I showed that with each second, he walks two additional meters. I then set up a proportion to figure out how many meters Juan walked in five seconds in he walks two meters per second. With both methods I found that Juan walked 10 meters in 5 seconds.
Web 2.0 Tools: Educreations whiteboard app, Google draw, online meter stick
10. Problem: A snake was 35 inches long. Now it is 57 inches long. How much did the snake grow?
Common Core Standard: 2.MD.B.5
Source: http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/grade2lengthwordproblems.pdf
Methods: write an equation, draw a picture
Mathematical Understanding: Students will develop their understanding of how to add lengths that are given the same units. It also gives students practice with solving equations with an unknown factor.
Solution: I first drew a picture to represent the original length and then the ending length of the snake. I labeled these measurements, which allowed me figure out how many inches the snake had grown. My next method was a write an equation to represent the snake’s growth. I used “x” to represent the unknown growth length in the equation. I then solved the equation and found that the value of “x” is 22 inches.
Web 2.0 Tools: online measuring stick, Google Draw, Educreations whiteboard app
11. Problem: Tom had 9 dimes. He bought a cupcake for 25 cents. How much money did Tom have left?
Common Core Standard: 2.MD.C.8
Source: http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/2ndgdmoneywordproblems.pdf
Methods: write an equation, draw a picture
Mathematical Understanding: This problem will allow students to practice solving word problems involving money quantities.
Solution: I first wrote an equation to represent the amount of money Tom started with, the amount of money he spent, and the amount of money he ended with. I knew that 9 dimes is 90 cents and used this knowledge to solve the equation. I then drew a picture of the currency and the money exchange. Tom started with 9 dimes (90 cents). He then paid for a 25 cent cupcake, which would require him paying with 3 dimes (30 cents). Tom would receive 5 cents back (I represented this with 1 nickel). Tom ends up with 6 dimes and 1 nikel, which is a total of 65 cents.
Web 2.0 Tools: “Money” (nlvm.usu.edu), Educreations whiteboard app, eManipulatives – “Coints and Bills” (eduplace.com)
12. Problem: Nathan threw a ball five feet. His friend then threw the ball three more feet. How far did the ball travel altogether?
Common Core Standard: 2.MD.B.5
Source: http://www.primaryjunction.net/2013/04/second-grade-common-core-measurement.html
Methods: draw a picture, write an equation
Mathematical Understanding: This problem gives students practice with adding two lengths identified by the same units.
Solution: My first method to solving with problem was drawing a picture. I drew Nathan throwing the ball 5 feet then drew his friend throwing it an additional 3 feet. I then added the total distance up to find that the ball traveled 8 feet altogether. My second approach was to write an equation adding two quantities that have the same units. This method also resulted in an answer of 8 feet.
Web 2.0 Tools: web whiteboard (https://awwapp.com/), Google Draw
Data Analysis
13. Problem: How many fewer bugs were caught on Saturday than were caught on Thursday?
Common Core Standard: 2.MD.D.9
Source: http://www.commoncoresheets.com/Math/Tally/Interpreting%20Graphs/1.pdf
Methods: write an equation, draw a picture
Mathematical Understanding: This problem gives students practice in reading and interpreting data from a graph. Students must then apply this data to answer questions.
Solution: I first wrote an equation to solve this problem. I looked at the chart to find the number of bugs on Saturday and Thursday. I then wrote a subtraction equation where I took away the number of bugs caught on Saturday from the number of bugs caught on Thursday to find that 28 more bugs were caught on Thursday. I then drew a picture illustrating this problem. I used circles to represent the number of bugs caught on both nights are counted how many more circles there were for Thursday than there were for Saturday.
Web 2.0 Tools: Educreation whiteboard app, Google Draw, “Color Chips – Subtraction” (nlvm.usu.edu)
Geometry
14. Problem: Which figure has more faces?
Common Core Standard: 2.G.A.1
Source: http://www.ixl.com/math/grade-3/count-and-compare-sides-edges-faces-and-vertices
Methods: draw a picture of the nets, using manipulatives
Mathematical Understanding: Students will get experience reasoning with shapes and their attributes. This will challenge students to compare the attributes of more than one three-dimensional figure.
Solution: My first approach to this problem was to draw the nets of the 3D figures. This gave me a visual of each side and made it easier to compare the number of sides in the two figures. I then made manipulatives that allowed me to look at the 3D objects and count the number of faces on each. Both methods led me to the solution that the second object has more faces than the first.
Web 2.0 Tools: virtual 3D shapes (nlvm.usu.edu), virtual 3D shape nets
15. Problem: We ordered a medium pizza, and we cut it into 8 slices. We ate 5 pieces. What fraction of pizza is left?
Common Core Standard: 2.G.A.3
Source: https://sites.google.com/a/g.coppellisd.com/missminton/fraction-word-problems
Methods: draw a picture, manipulatives
Mathematical Understanding: This problem promotes student understanding of shapes as they work with shapes and their attributes to solve word problems that involve fractions.
Solution: To figure out the fraction of the pizza that is left after 5 pieces have been eaten I drew a picture. The green segments represent eaten pizza. The blue segments represent remaining pizza. I found that out of 8 slices, 3 were left. So 3/8 of the pizza were left over. I then created a manipulative to use to help visualize the problem. The orange pizza pieces represent pizza slices that have been eaten. In this hands-on approach I also found that 3/8 of the pizza is left over.
Web 2.0 Tools: “Fractions – Part of a Whole” virtual manipulatives (nlvm.usu.edu), Fraction Circle app, Google Draw, Educreations whiteboard app